Overview of selected scams - March 2024
We present the report on identified threats and the methods of operation by criminals for the month of March 2024. This document highlights selected risks to customers of Polish banks. We encourage you to review the material. The document does not cover threats that have been known for many months and were described in an earlier report, such as the "classicscam", fake Facebook login panels, fake shops and other. It is essential to remember, however, that these scenarios are still being used by criminals, and we must continually work against them.
False investment schemess
A well-known but still very popular criminal scenario is fake investments. It's a scam scheme in which cybercriminals impersonate well-known individuals or institutions. They aim to persuade people to invest their money. In reality, their goal is to expose the victim to high financial losses.
Criminals still eagerly utilize deepfake technology to create deceptive materials. They use the images of well-known individuals to generate video recordings promoting supposed investments (Fig. 1-2).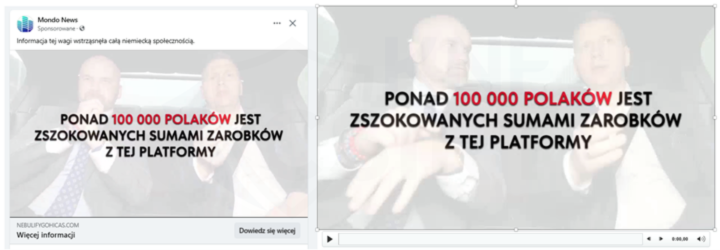
Figure 1 The use of deepfake technology to create deceptive content 1/2
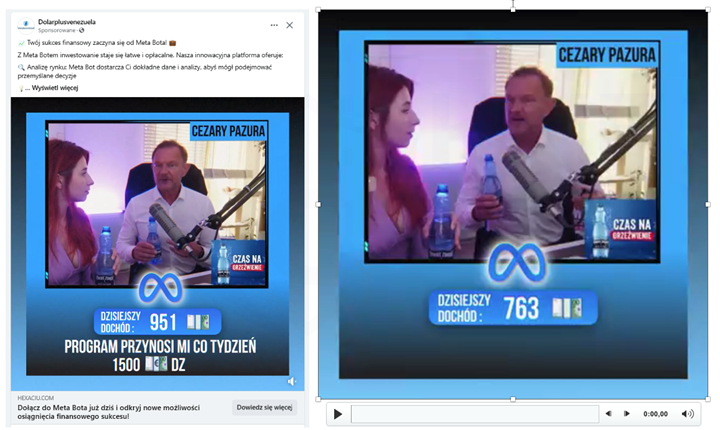
Figure 2 The use of deepfake technology to create deceptive content 2/2
False offers (both in the form of video recordings and static ads) are distributed through:
- ads on the Facebook platform (Fig. 3),
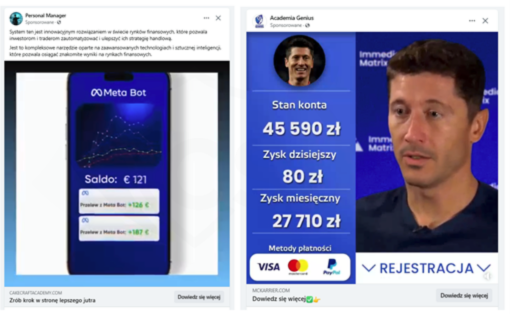
Figure 3 Fake investment - ads on the Facebook platform
- ads on the X (formerly Twitter) platform (Fig. 4),
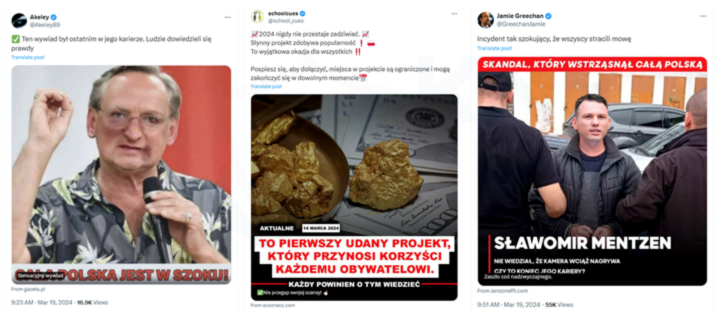
Figure 4 Fake investment - ads on the X platform
Upon clicking on each of the previously shown links, the victim is directed to a webpage where they enter their contact information (Fig. 5). It also happens that the form is directly on Facebook.
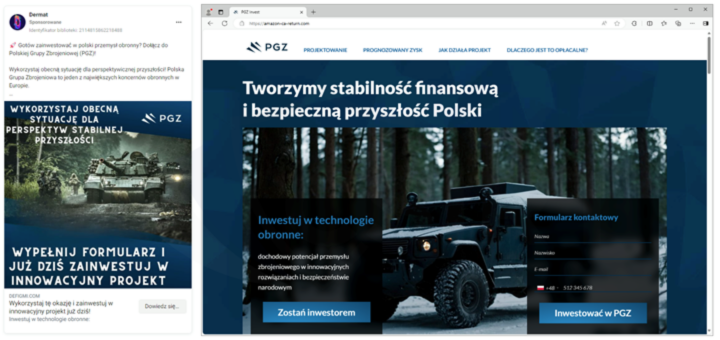
Figure 5 False investments - phishing site
The data obtained by cybercriminals in this way enables them to establish contact with the manipulated person, then stealing their money. Many people still fall for this scenario, so it is very important to take actions aimed at countering it.
IMPERSONATING POLISH BANKS
Criminals regularly impersonate banks to extract information about payment cards and authentication data for online banking. They also encourage downloading malicious applications. In March 2024, criminals also utilized this method of operation.
Criminals publish ads on the Facebook platform, impersonating Polish banks. Under the pretext of claiming a reward or the necessity of updating an application, they attempt to phish authentication data for online banking and payment card details.
Appearance of the ads published on the Facebook platform (Fig. 6):

Figure 6 Ads impersonating polish banks
Appearance of the ads and phishing sites (Fig. 15-17):

Figure 7 Fake ads and phishing sites - impersonating polish bank
Fake SMS messages and phishing sites are used for cybercrime:
- impersonating Millennium Bank (Fig. 8):
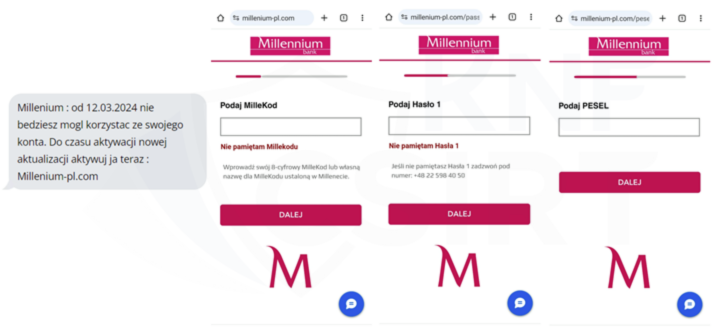
Figure 8 Fake SMS and phishing sites - impersonating Millennium Bank
- impersonating ING Bank (Fig. 9):
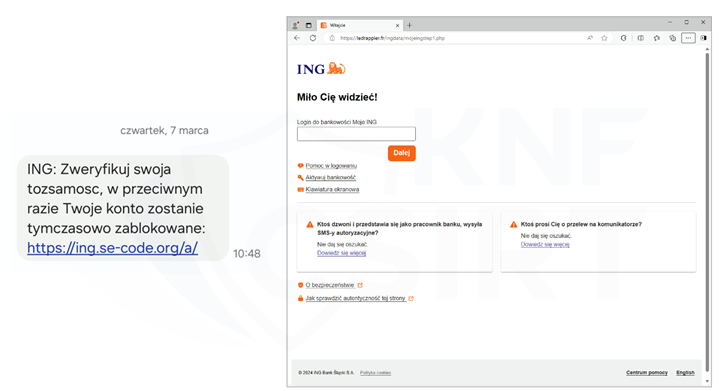
Figure 9 Fake SMS and phishing site - impersonating ING Bank
- impersonating BNP Paribas (Fig. 10):
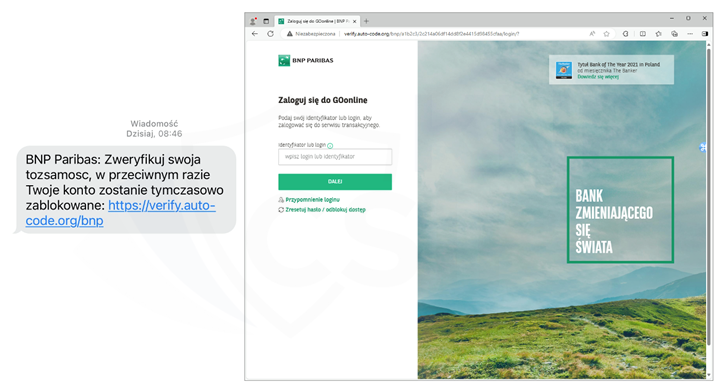
Figure 10 Fake SMS and phishing site - impersonating BNP Paribas
Appearance of a phishing sites impersonating polish banks (Fig. 11-13).
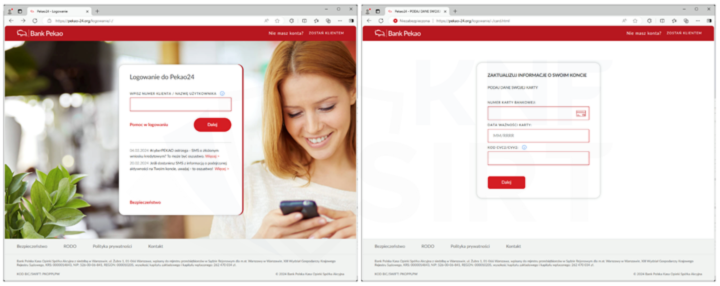
Figure 11 Phishing sites - impersonating Pekao
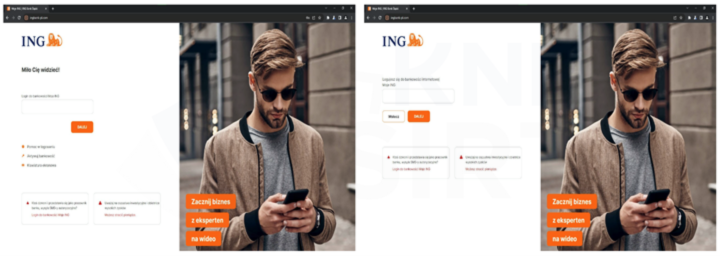
Figure 12 Phishing sites - impersonating ING
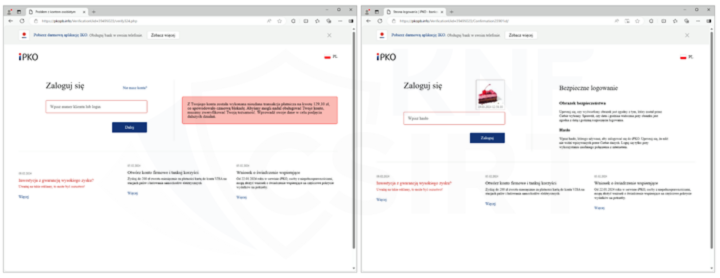
Figure 13 Phishing sites - impersonating PKO
"TAX REFUND CONFIRMATION", GOVERNMENT WEBSITE IMPERSONATION
Criminals, impersonating government site, they informed about a supposedly approved tax refund application and the possibility of receiving money after data verification. They encouraged clicking on a link that, in reality, led to a phishing site. In this way, the fraudsters aimed to obtain information about payment card details.
Fake email message (Fig. 14):
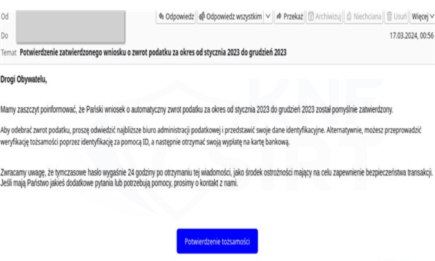
Figure 14 Fake email, source: https://twitter.com/CERT_Polska/status/1769654859664416871
Phishing site (Fig. 15):
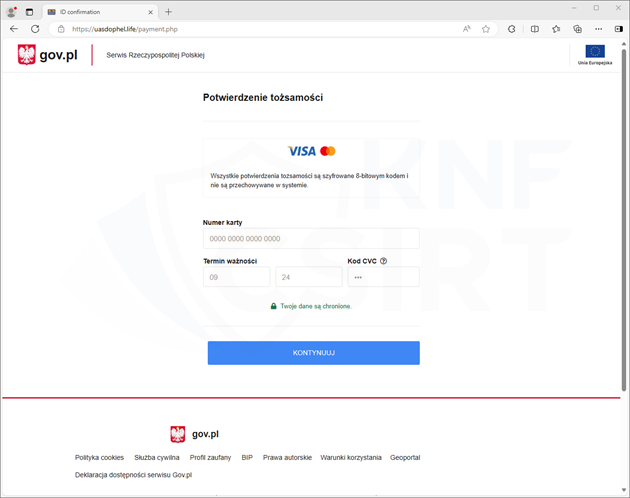
Figure 15 Phishing site - impersonating goverment website
WROCŁAW CITY CARD
Criminals set up phishing websites impersonating city of Wrocław. They informed about a supposed opportunity to purchase a personalized city card. To take advantage of the promotion, they encouraged clicking on a link. This link led to a fake website, where fraudsters tried to obtain information about the payment card (full card number, CVV code, and expiration date).
Ads of the Facebook platform (Fig. 16):

Figure 16 Fake ads od the Facebook platform
Phishing sites used in the described campaign (Fig. 17):
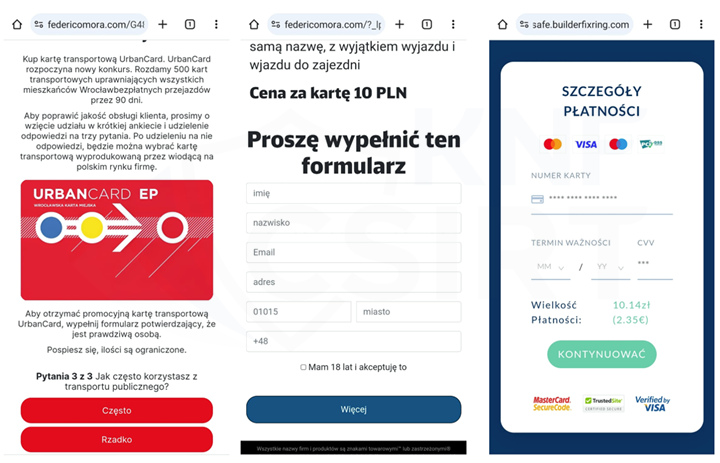
Figure 17 Phishing sites - impersonating city of Wrocław
"OVERDUE HIGHWAY TOLLS” – IMPERSONATING E-TOLL
Criminals prepared a phishing campaign and informed about a supposed necessity to pay overdue bills for highway tolls. To avoid alleged further consequences, they encouraged clicking on a link. This link led to a fake site where fraudsters tried to obtain information about the payment card.
SMS message containing a phishing site (Fig. 18):
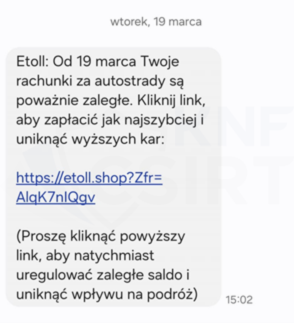
Figure 18 Fake SMS - impersonating e-Toll
Phishing sitea (Fig. 19):
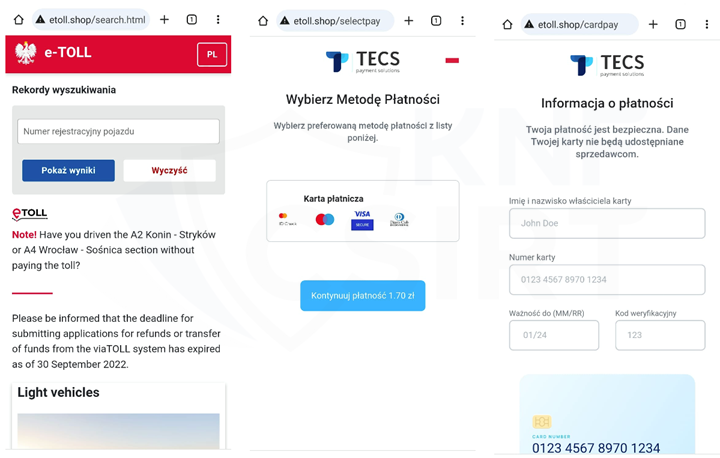
Figure 19 Phishing sites - impersonating e-Toll
IMPERSONATING COURIER COMPANIES
Criminals once again prepared a phishing campaign impersonating courier companies. This time, they used the image of InPost and DHL. Phishing sites were distributed through SMS messages. On the fake site, personal data and information about payment cards were solicited.
Fake SMS messages and phishing sites (Fig. 20-21):
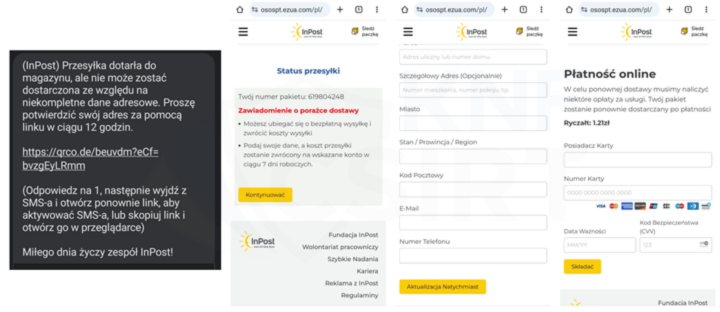
Figure 20 Fake SMS and phishing sites - impersonating InPost
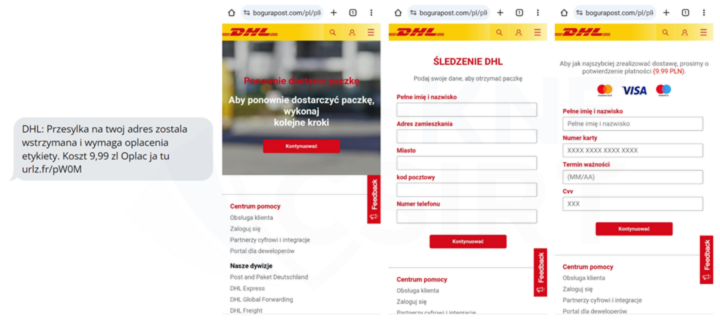
Figure 21 Fake SMS and phishing sites - impersonating DHL
NO ACESS TO INTERNET TELEVISON
Criminals prepared a phishing campaign impersonating Netflix and HBO. By informing that the subscription had supposedly expired, they encouraged clicking on a link. On the fake site, personal data and information about payment cards were solicited.
Example SMS message impersonating Netflix (Fig. 22):
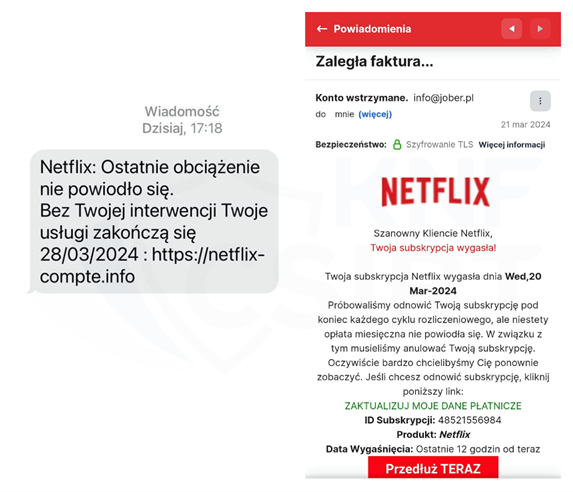
Figure 22 Fake SMS message and phishing site - impersonating Netflix
Example email message impersonating HBO (Fig. 23):
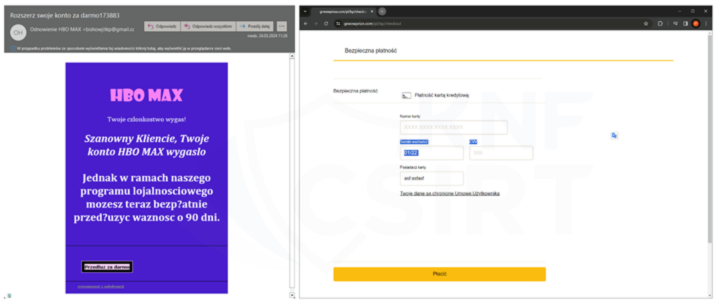
Figure 23 Fake email message and phishing site - impersonating HBO
"FRIENDLY REMINDER" - IMPERSONATING SPOTIFY
Criminals prepared a phishing campaign impersonating Spotify. Informing that an invoice needs to be paid, they encouraged clicking on a link contained in the email. On the fake site, personal data and information about payment cards were solicited.
Example email message and phishing site impersonating Spotify (Fig. 24):
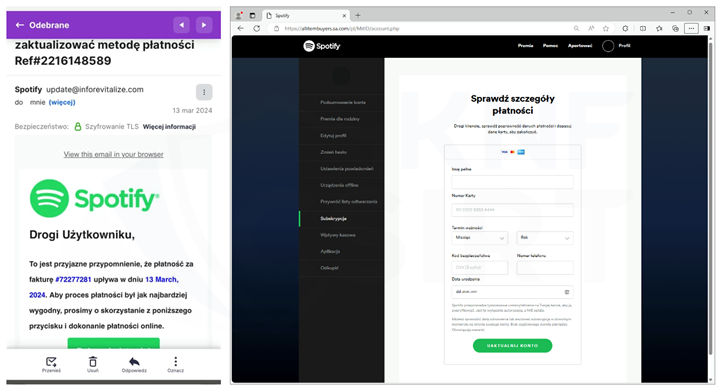
Figure 24 Fake emial and phishing site - impersonating Spotify
Yet another month of this year has demonstrated that criminals are constantly refining their methods of operation. We consistently believe that conducting informational and educational activities is crucial.
That's why news about cyber threats and fraudulent trends are also published on the following our social media platform: Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook.

